Global Issues
Everything You Need To Know About The Menstrual Cycle -By Muhammad Muawiya Alkali
INTRODUCTION
The reproductive life of a woman begins with menarche and ends with menopause. At the beginning of menarche (around the age of 8 to 14), short term bleeding at irregular intervals are noticed which last for one (1) to several years, so also at the onset of menopause (around the age of 45 to 50).
Menstruation is a characteristics of primates and do not not occur in any other vertebrates. Menstrual cycle is the period between successive menstrual flows. The cycle is an average of 28 days in women (may be 20 to 32 days) as it varies from individual to individual. About every 28 days, some blood and other products of the disintegration of the inner lining of the uterus (the endometrium) are discharged from the uterus in a process called menstruation or menstrual flow.
HORMONAL INTERPLAY IN MENSTRUAL CYCLE
Cyclic release of pituitary gonadotropins; Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH) regulate changes in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina, which is in turn, controlled by the hypothalamic Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH). FSH and LH stimulates the gonads to produce the sex steroids; estrogens and progesterone.
The rise in estrogens level causes the endometrium to become thicker and richly supplied with blood vessels and glands.
Rise in the level of LH causes developing egg within the follicle to complete the first meiotic division (Meiosis I), forming secondary oocyte. Ovulation takes place in about two weeks, after a rapid rise in level of LH. Ovulation is the release of secondary oocyte from one of the ovary into the fallopian tube. The follicle, which becomes empty after ovulation, develops into a Corpus luteum under the influence of LH. Progesterone is secreted by Corpus luteum as a result of stimulation by LH; progesterone continues the preparation of the endometrium for a possible pregnancy, it also inhibit uterine contraction and the development of a new follicle.
If fertilization does not occur, the rising level of progesterone inhibits the release of GnRH which consequently inhibit production of progesterone (feedback inhibition). As progesterone level drops, the Corpus luteum begins to degenerate and regress, the endometrium begins to breakdown and it undergo apoptosis. Inhibition on the uterine contraction is also lifted, hence bleeding and cramps of menstruation begins.
Therefore, menstruation in normal females take place when the Corpus luteum is regressing i.e withdrawal of progesterone.
PHASES OF MENSTRUAL CYCLE
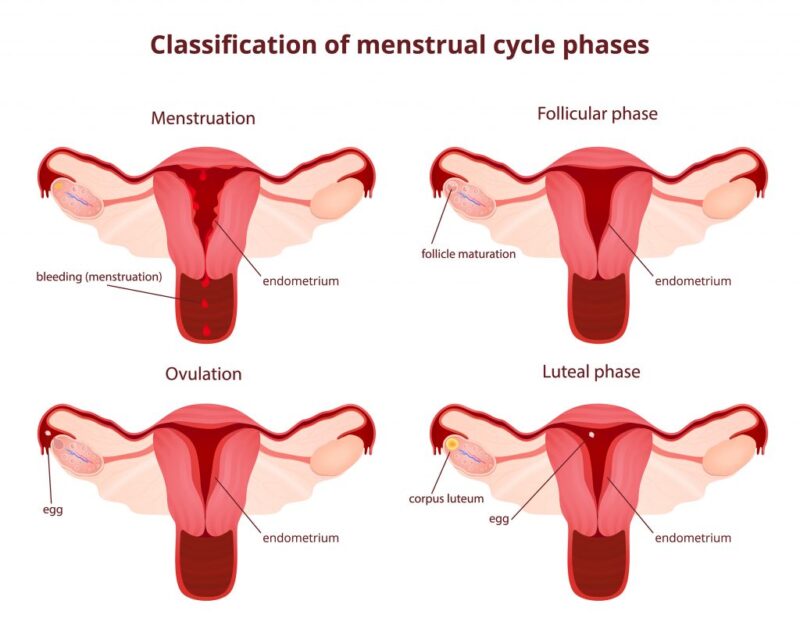
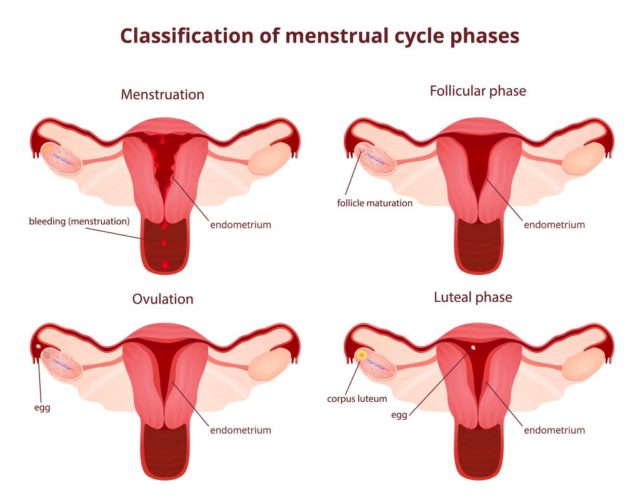
There are four phases of the menstrual cycle: Mentrual phase, Follicular (Proliferative) phase, Ovulatory phase and Luteal (Pregestational) phase.
Menstrual Phase: This phase is represented by 4 to 7 days of vaginal bleeding during which the superficial layer of the endometrium are shed off. Regression of the Corpus luteum and decline in the level of progesterone causes the uterine mucosa to become thinner, spiral arteries become exposed and bleeding from them begins which lead to local necrosis and desquamation.
Follicular phase: This phase last from the end of menstrual phase to ovulation (mid-cycle). Development of new follicle is initiated in the ovary by the action of FSH and LH during the end of the menstrual flow. The uterine endometrium cells proliferate and thickens as estrogens level rise. Basal arteries proliferate into new vessels, vaginal mucosa becomes thicker and permit free passage of spermatozoa.
Ovulatory phase: A critical level of estradiol secretion triggers a surge release of FSH and LH which induce ovulation 24 to 36 hours later. This occurs at about 2 weeks before the onset of the next menstruation but may vary with individual.
Luteul phase: Follicular cells get luteinized and start secreting estrogens and progesterone after ovulation which result to a decrease in secretion of FSH and LH. Uterine endometrium prepare for implantation of embryo and vaginal epithelium get profusely infiltrated by leukocytes.
In the absence of implantation, the Corpus luteum starts regressing about 10 days after its formation which result to fall in the level of circulating sex steroids and the uterine endometrium undergoes degenerative changes. Leukocytes invade the tissue, necrosis occur, uterine glands involute and sloughing off of the uterine mucosa accompanies and eventually menstrual flow.
CONCEPTION AND SAFE WINDOW
Menstrual Phase
Duration: 4 to 7 days
Main activity: Vaginal bleeding.
Probability of pregnancy: Almost zero chances of conception.
Recommendation: Sex is not recommended in this period as there is high tendency of infection and vaginal-penile penetration may be painful.
Follicular Phase
Duration: 7 to 10 days
Main activity: Follicle development.
Probability of pregnancy: Zero chances of pregnancy at the beginning of this phase but may increases towards the end (upto 50%).
Recommendation: Couples controlling birth using the cycle should avoid sex towards the end of this phase (i.e 5 to 7 days after cessation of bleeding) because the lifespan of sperm is about 5 days on average. Couples that want pregnancy however, should often have sex during this phase.
Ovulatory Phase
Duration: 24 to 36 hours
Main activity: Release of ovum or egg near the middle of the cycle (day 14) or 2 weeks before the onset of the next bleeding. It can occur as close as 9 days or as far as 20 days before the next cycle.
Probability of pregnancy: Very high chances of pregnancy during ovulation (about 50% to 70%) and almost 100% chance immediately after ovulation because the ovum can last for about 24 hours and fertilization takes place when the ovum is moving from the ovary through the fallopian tube before it reaches the uterus except in ECTOPIC pregnancy.
Recommendation: Sex is highly recommended for couples in need of pregnancy and should be avoided by couples adopting birth control using the cycle around this period because sperm can stay for a week in the system waiting for an egg to be released.
Luteal Phase
Duration: 10 to 12 days
Main activity: Regression of the Corpus luteum and decline in levels of sex steroids.
Probability of pregnancy: Chances of pregnancy is high at the beginning (first 2 days) of this phase but it decreases to zero towards the end of the phase as the vagina undergo changes that makes it impermeable to spermatozoa.
Recommendation: Sex is recommended for couples using the cycle to control birth from the middle onward till the onset of bleeding.
CONCLUSION
These recommendations and probabilities of pregnancy mentioned above are based on the assumption that:
The menstrual cycle is 28 days on average (which may be 20 to 32 days).
Bleeding last for 4 to 7 days (which may last for only 1 day or 15 days).
Ovulation occur at the middle of the cycle i.e around 14 days before the onset of the next bleeding (which may be as close as 9 days or as far as 20 days before the next cycle).
An egg or ovum stays for an average of 24 hours.
The lifespan of sperm is 5 days (which may be 2 to 7 days).
However, factors other than the ones mentioned above influence the chances of conception, these include but not limited to age (females in their twenties are more fertile than those above 35 as fertility decline steeply from mid-thirties onward), diet, body temperature and pH, physiological state and stress. Therefore, couples should not get obsessed with the struggle to conceive as it induces stress which subsequently interfere with the chances of conception, rather couples should enjoy good sex, eat healthy diet and maintain a good condition of health through frequent exercise and adequate rest. It is also advisable for the woman to lie down for 20 to 30 minutes after sex so that the sperm can swim easily to their destination.

















